Innovative Gyros Set for Martian Moons Exploration Mission
silicon Sensing Systems ltd has secured a contract with the German Aerospace Center (DLR) to provide two miniature Pinpoint® (CRM200) gyroscopes for the Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission.
Mission Overview
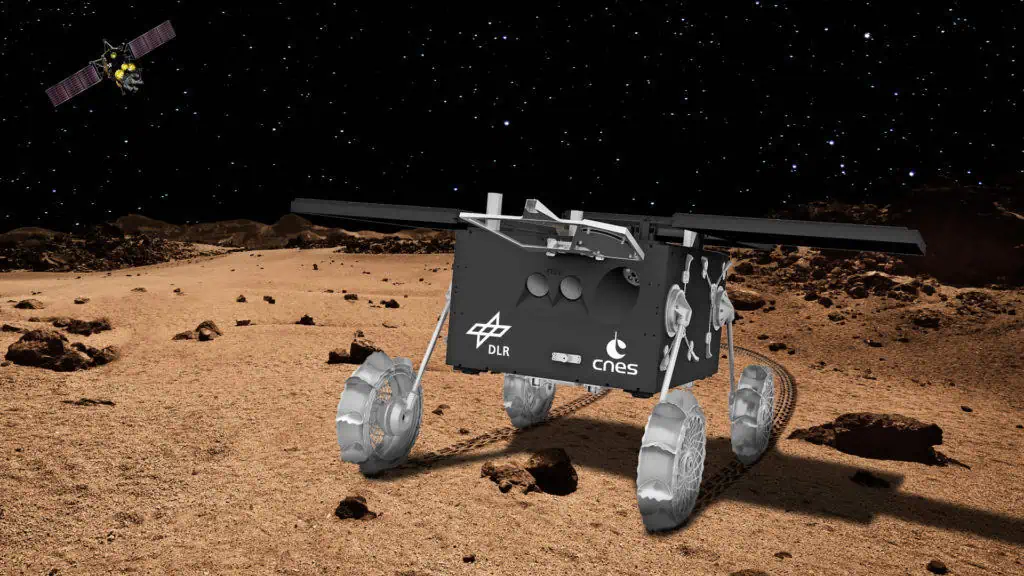
This ambitious mission aims to investigate Mars’ two moons,utilizing these gyros to enhance the rover’s capabilities as it explores Phobos,the larger of the two moons,and gathers essential surface samples.
gyro Functionality and Safety Features
The Pinpoint gyros will play a crucial role in monitoring any unintended movements of the rover on the unfamiliar terrain. Based on the initial assessment of the drivetrain, which incorporates these gyros, an optional safety feature can be activated in the software to automatically mitigate instability during the rover’s operational phases.
Proven Reliability in Space Conditions
As part of a stringent selection process, the Pinpoint gyros successfully underwent TID testing at 17kRad Radiation and Proton tests (up to 68 MeV/proton), confirming their suitability for the harsh conditions of space.
Compact Design and Versatility
Measuring just 5mm x 6mm, the pinpoint® gyros are the smallest in Silicon Sensing’s MEMS product line. These low-drift, single-axis angular rate sensors are versatile, finding applications across various sectors.
These robust sensors can accurately measure angular rates across multiple axes, including pitch, yaw, and roll, while maintaining low power consumption.
Collaborative Efforts in Space Exploration
The MMX mission is spearheaded by the japanese space agency JAXA, with meaningful contributions from NASA, ESA, CNES, and DLR. Notably, CNES and DLR are jointly developing a 25kg rover under their collaborative leadership.
Mission Timeline and Objectives
Approximately one year post-launch, the spacecraft is expected to reach Martian orbit, subsequently transitioning into a quasi-satellite orbit around Phobos. Here, it will collect scientific data, deploy the rover, and gather surface samples.
Following the collection of samples, the spacecraft will return to Earth, with the current timeline indicating a launch in 2026, Martian orbit insertion in 2027, and a return to Earth in 2031.
Expert Insights
David Sommerville, General Manager at Silicon Sensing Systems, remarked, “Pinpoint has a strong history in space applications, and this mission represents a significant milestone where the gyro’s reliability and durability will be paramount.”
“We are also witnessing a surge in interest for our latest tactical-grade IMU – the DMU41 – which has been selected for several low Earth orbit initiatives. This growing demand for our MEMS-based inertial sensors highlights the technology’s potential, characterized by its robust reliability, compact form factor, and low energy consumption.”

























