Understanding RCV Engine Technology
The term “RCV” in RCV Engines stands for Rotating Cylinder Valve, a designation that originated when the company first entered the hobby engine market in 1997.
Although the original model engines are no longer in production and the technology has advanced considerably, the RCV name remains relevant today.
Modern Engine Design
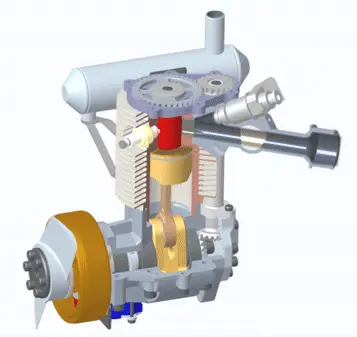
Contemporary RCV engines feature a valve that rotates within a cylinder bore, driven by a crank mechanism. This design marks a significant evolution from earlier models, which utilized a rotating sleeve that housed the valve.
Advantages of RCV Technology
One of the standout features of RCV engines is their combustion system, frequently enough hailed by experts as “almost flawless.” This remarkable combustion mechanism distinguishes RCV Engines from other engine technologies. To delve deeper into its workings, continue reading.
The combustion system is crucial as it facilitates the mixing of air and fuel, igniting it within a chamber to generate mechanical power through increased pressure.
Key Characteristics of an Ideal Combustion System
For optimal performance, a combustion system should exhibit two primary traits:
- The air and fuel must be mixed thoroughly, ensuring that every bit of fuel has access to oxygen for complete combustion.
- The combustion chamber should have a compact design, which minimizes heat loss to the engine body and allows the flame to spread quickly throughout the mixture.
How RCV Engines Meet These Standards
The rotating valve design of RCV engines effectively meets both of these ideal characteristics. The valve’s rotation creates significant turbulence, ensuring thorough mixing of air and fuel. Additionally, the combustion chamber is compactly housed within the rotating valve body.
The result is that RCV engines are not only easy to start but also deliver impressive power and reliability, whether using gasoline or heavier fuels like JET A1, JP5, or JP8. Moreover, all RCV engines are high-performance four-stroke models, producing power comparable to two-stroke engines while being 30% to 50% more fuel-efficient for similar tasks.
Maintenance and Longevity
Another advantage of RCV engines is their low maintenance requirements and extended service intervals. The straightforward rotary motion of the valve eliminates the need for adjustments. Additionally, the spark plug is shielded from much of the combustion process, reducing carbon buildup. Consequently, service intervals can extend to approximately 250 hours.


























