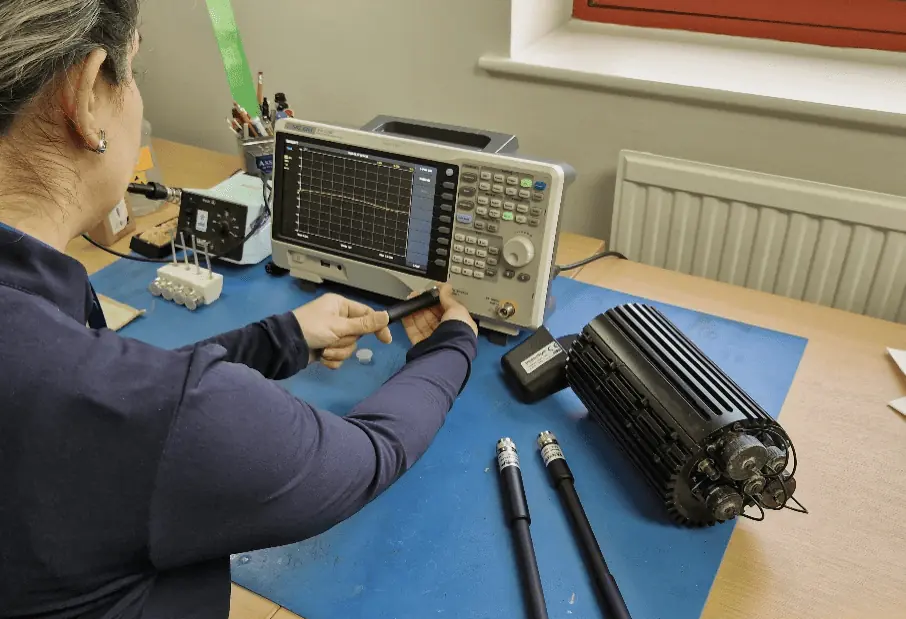
VB Antennas highlights essential factors to consider when choosing the ideal antenna for your needs, emphasizing the support the company offers.
Choosing the right antenna is crucial for ensuring it aligns with your specific needs. With a diverse array of antennas available,the significance of making an informed selection cannot be overstated. An inappropriate choice can lead to significant issues, including compromised signal transmission and reception. Additionally, environmental factors play a vital role in antenna selection. Antennas not designed for specific conditions may detach or fail, complicating the selection process. To aid in your decision-making, here are seven crucial factors to consider when selecting an antenna, along with how VB Antennas can assist you.
Understanding Frequency
The frequency of an antenna indicates the rate at which it transmits or receives electromagnetic waves, determining the types of signals it can manage effectively. Antennas are tailored to function at specific frequencies or ranges. Various antennas are optimized for distinct frequency bands, including FM radio, SHF (L, S, and C Bands), television, mobile communications (like 4G and 5G), Wi-Fi, and satellite communications. Each frequency band necessitates a unique antenna design to ensure efficient signal transmission and reception.
Frequency Bandwidth
Antennas are meticulously designed to perform best within a specified frequency range. The bandwidth of an antenna refers to the spectrum of frequencies where it meets certain performance criteria, such as gain, radiation pattern, and VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio). VSWR is frequently enough used to evaluate bandwidth, leading to the term “impedance bandwidth” to describe this frequency range.
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)
VSWR measures the degree of impedance matching between the antenna and the connected radio or transmission line, indicating the amount of power reflected back. A lower VSWR signifies reduced loss between the antenna and transmission line, enhancing power delivery. VSWR values range from 1 to infinity,with a value of 2 or less generally considered acceptable for most applications. A VSWR of 1:1 indicates no reflected power, while the industry standard is 2:1, allowing for a maximum of 11% reflected power.
Antenna Gain
Antenna gain reflects its ability to direct or concentrate transmitted or received electromagnetic energy in a specific direction compared to an isotropic radiator, which disperses energy uniformly. Gain is quantified in decibels (dBi), with higher values indicating a more focused antenna capable of efficiently transmitting or receiving signals in the desired direction. However, higher gain dose not always equate to better performance; the effectiveness of an antenna is influenced by various factors, including the application and installation site.
radiation Patterns
The radiation pattern of an antenna illustrates the spatial distribution of electromagnetic energy it radiates or receives. This pattern provides insights into the antenna’s directional capabilities, indicating its sensitivity and the direction of maximum radiation or reception. Antennas can be either directional or omnidirectional. Omnidirectional antennas are designed to radiate and receive energy effectively in all horizontal directions, making them ideal for applications requiring broad coverage. In contrast, directional antennas focus energy in a specific direction, which is beneficial in scenarios where comprehensive coverage is not necesary.
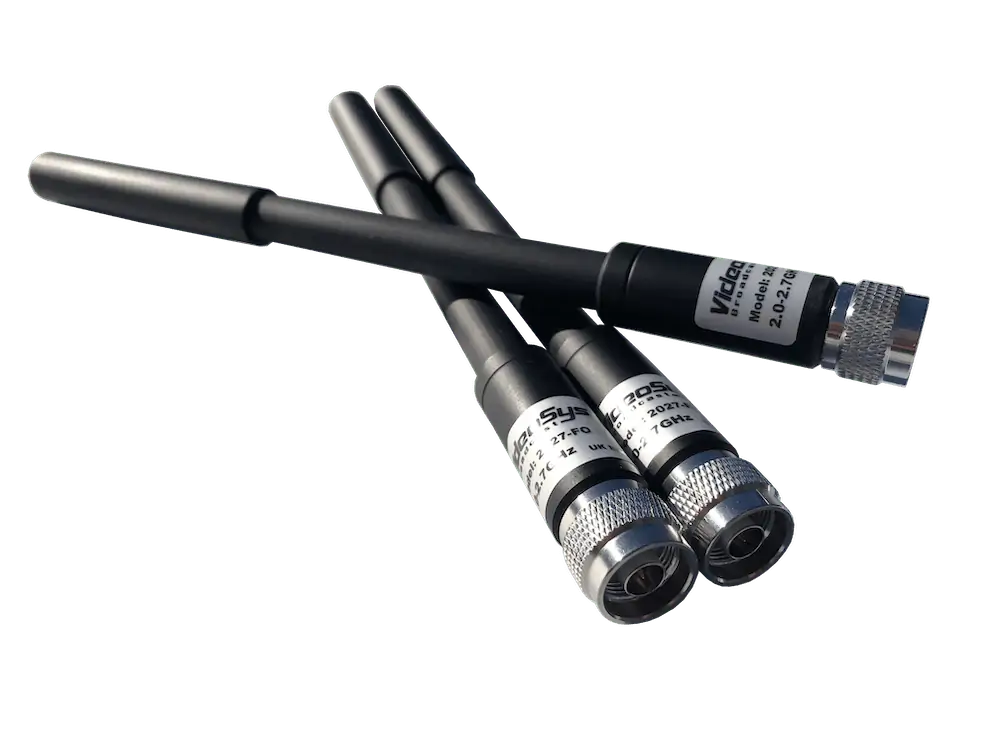
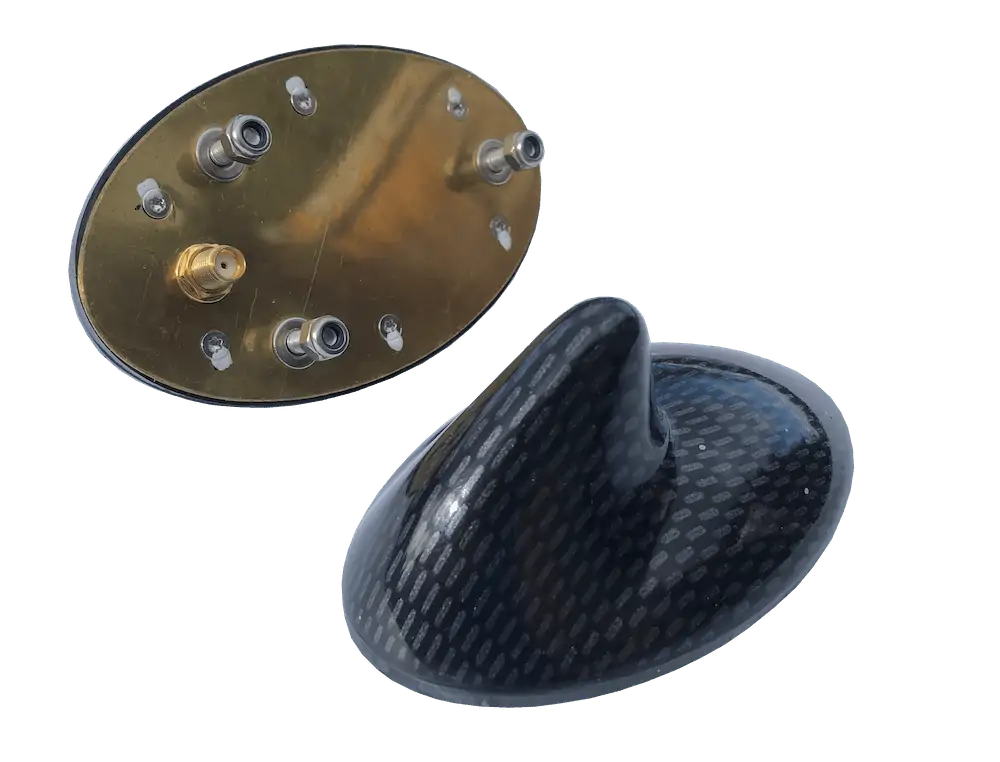
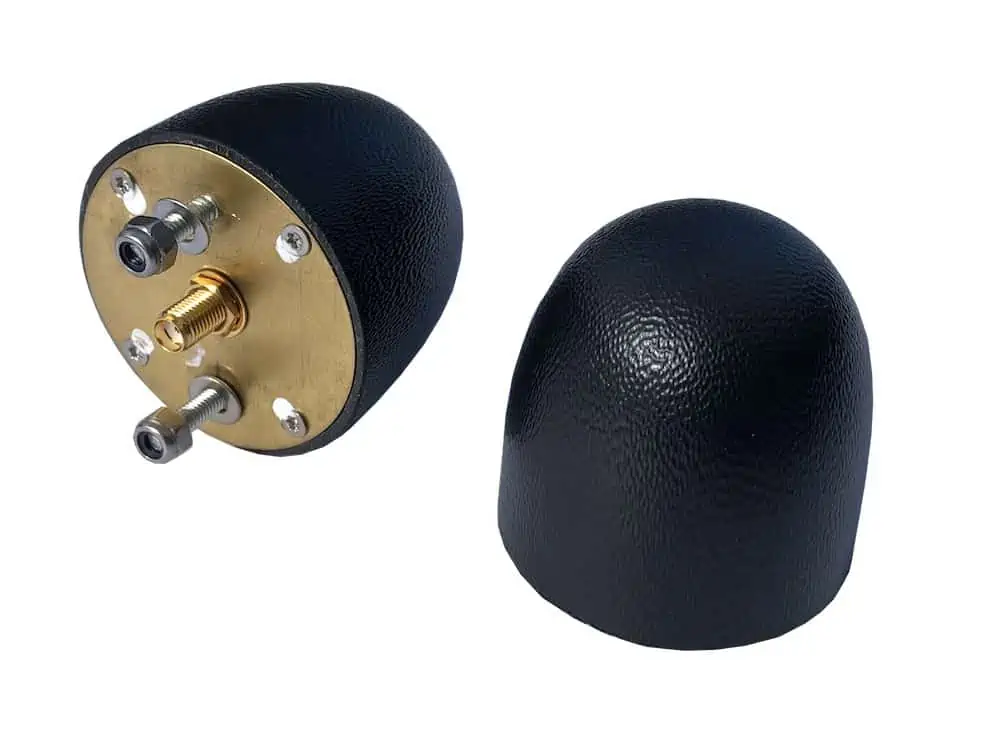
Mounting Options
Mounting refers to how an antenna is physically installed or attached to a structure. The method and location of mounting significantly influence antenna performance. Factors such as antenna type, desired coverage area, installation habitat, and specific application requirements dictate the choice of mounting. Common mounting options include:
- roof Mount: Antennas can be installed on rooftops using brackets or mast systems;
- Wall Mount: Antennas can be affixed directly to walls or vertical surfaces with brackets or specialized mounts;
- Ground Mount: Antennas can be placed directly on the ground using ground plane mounts or stakes.
Proper mounting is essential for optimizing antenna performance, minimizing signal loss, and ensuring stability.Considerations such as antenna height,orientation,and nearby obstacles are crucial for achieving the desired coverage and signal strength.
Optimal Placement
The placement of an antenna is influenced by various factors,including its type,intended use,and the surrounding environment. Key considerations include height, clear line of sight, interference avoidance, orientation, grounding, and compliance with regulations. Antennas can be designed for indoor or outdoor use, with outdoor antennas typically featuring protective housing to shield against environmental elements and ensure optimal functionality.
For expert advice and guidance on selecting the right antenna, reach out to VB Antennas.