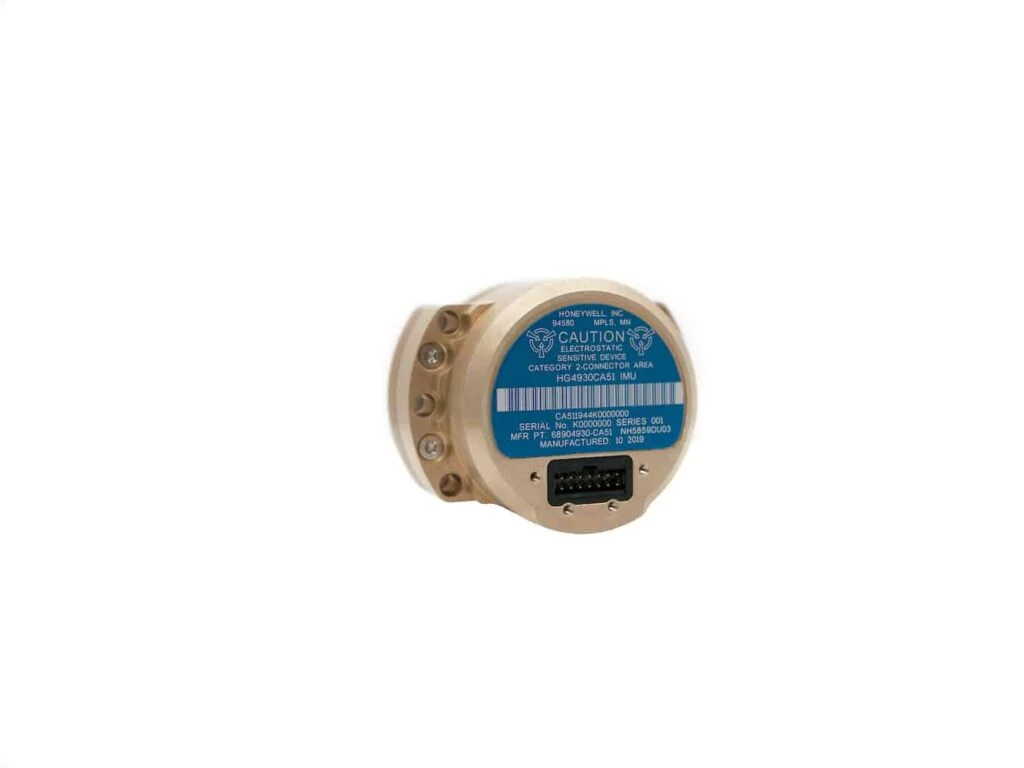
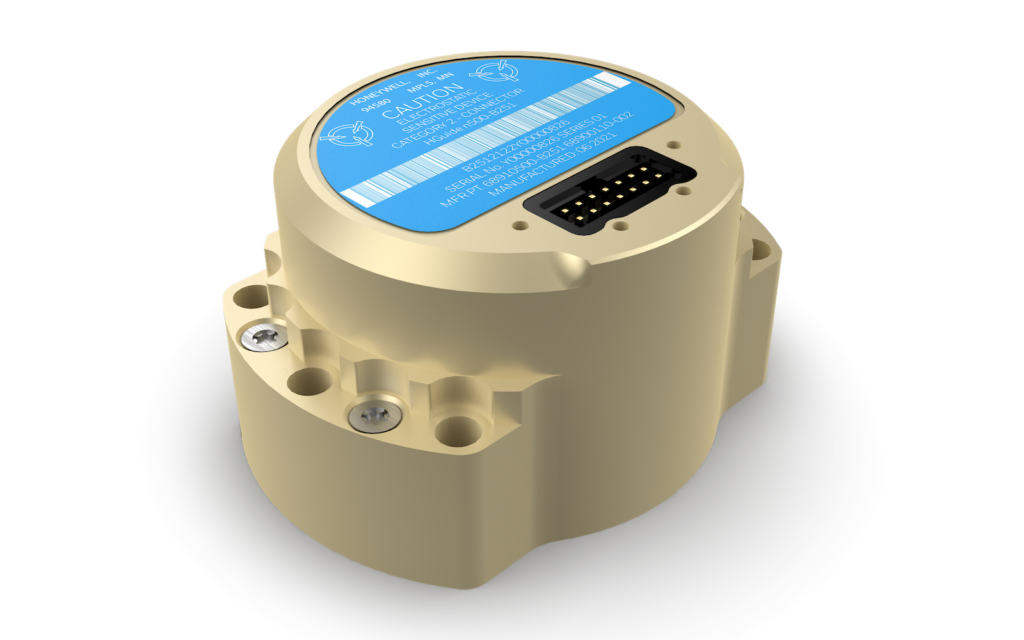
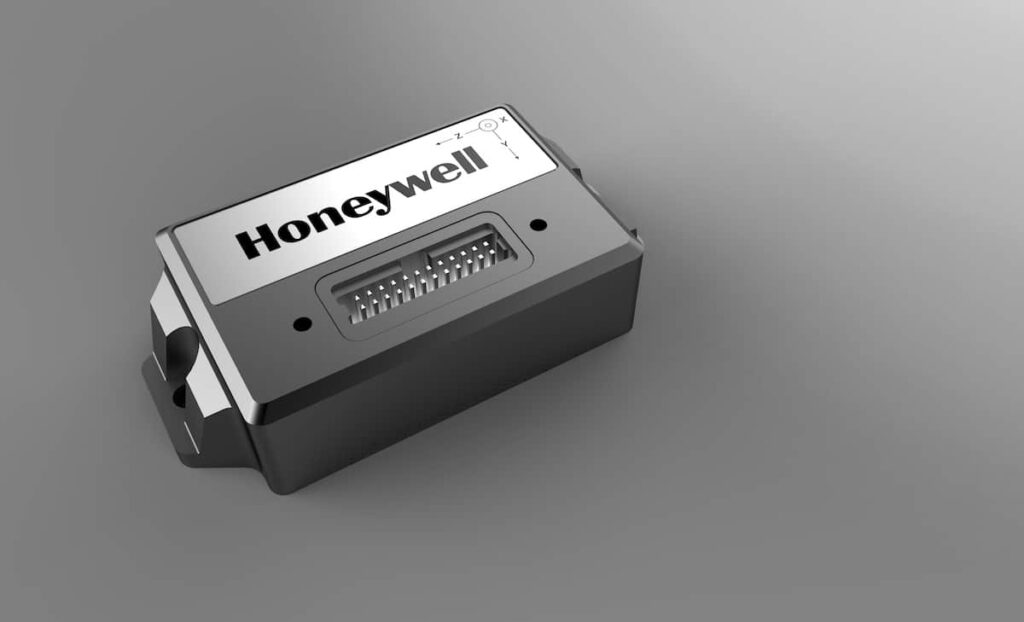
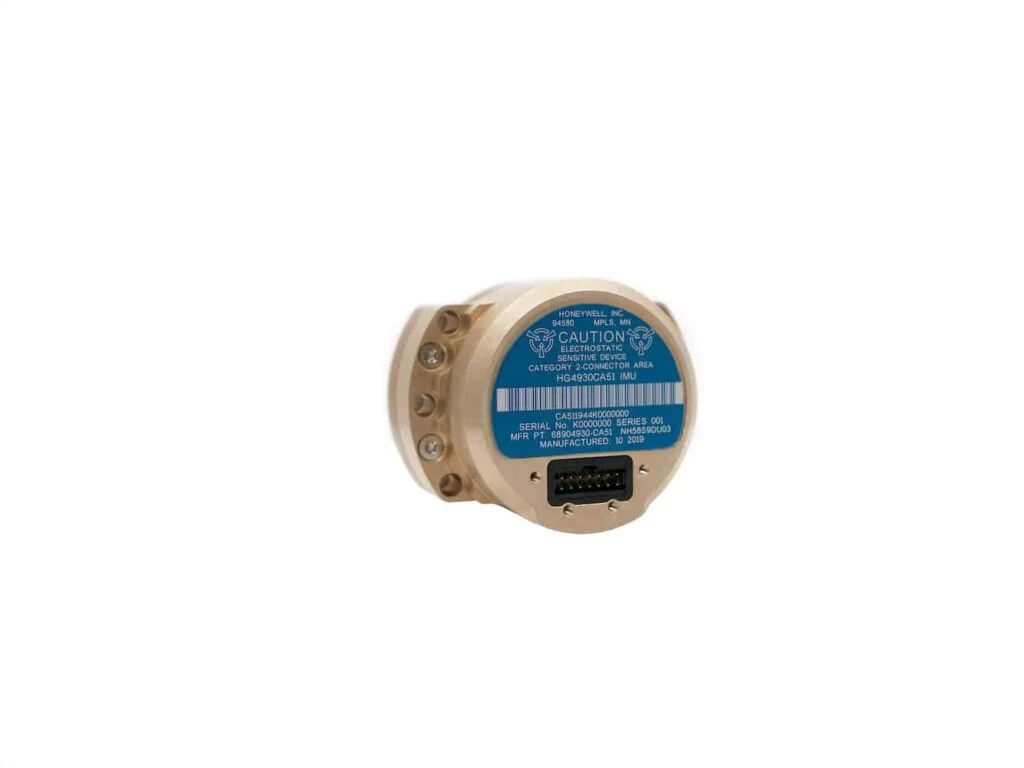
Introducing the HGuide HG4930: A Cutting-Edge MEMS IMU
The HGuide HG4930 stands out as the most efficient MEMS Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) available, offering exceptional performance relative to its size and cost. This advanced unit serves as a modern alternative to traditional, larger Fiber optic Gyroscope (FOG) systems. Tailored for various applications, including Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs), Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), and other robotic systems, its remarkably compact size, lightweight design, and low power consumption make it a versatile choice for numerous platforms and configurations.
This robust sensor solution features cutting-edge calibration and compensation technologies, along with a unique internal environmental isolation mechanism that minimizes interference from external factors. Users can customize settings such as filtering options, output data rates, and dialog protocols to suit their specific needs.
The HGuide HG4930 is offered in three distinct performance tiers,catering to a variety of operational requirements.
Technical Specifications
| HG4930CA51/CB50 | HG4930BA51 | HG4930AA51 | |
| Dimensions/Volume | 65 x 51 x 35.5 mm / 82 cm³ (5 in³) | 65 x 51 x 35.5 mm / 82 cm³ (5 in³) | 65 x 51 x 35.5 mm / 82 cm³ (5 in³) |
| weight | 140g (0.3 lbs) | 140g (0.3 lbs) | 140g (0.3 lbs) |
| Power Supply | 5 VDC, < 2W | 5 VDC, < 2W | 5 VDC, < 2W |
| Gyroscope Range | ±400 deg/s across all axes | ±400 deg/s across all axes | ±400 deg/s across all axes |
| Accelerometer Range | ±20g across all axes | ±20g across all axes | ±20g across all axes |
| Gyro Bias Repeatability | 7°/hr 1σ | 10°/hr 1σ | 20°/hr 1σ |
| Gyro Bias In-run stability | 0.25°/hr 1σ | 0.35°/hr 1σ | 0.45°/hr 1σ |
| Angular Random Walk (ARW) | 0.04°/√hr | 0.05°/√hr | 0.06°/√hr |
| Accelerometer Bias Repeatability | 1.7 mg 1σ | 2.0 mg 1σ | 3.0 mg 1σ |
| Accelerometer Bias In-run Stability | 0.025 mg 1σ | 0.05 mg 1σ | 0.075 mg 1σ |
| Velocity Random Walk (VRW) | 0.03 m/s/√hr | 0.04 m/s/√hr | 0.06 m/s/√hr |