Maxtena specializes in cutting-edge passive and active antennas designed for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs).
These antennas are integral too contemporary communication frameworks, serving as essential elements for the transmission and reception of electromagnetic signals.
Choosing the appropriate antenna is vital for maximizing the efficiency of any communication setup. an effective antenna must transmit or receive signals proficiently to minimize power loss and enhance overall performance.
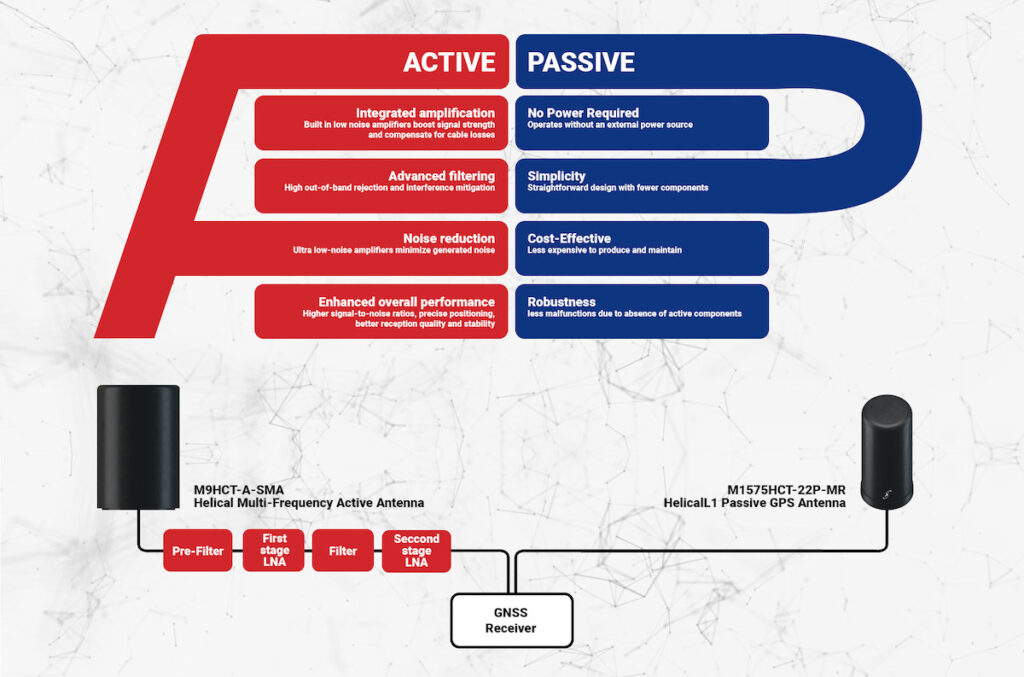
Understanding Active antennas
Active antennas incorporate a built-in Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) that boosts weak incoming signals. This LNA requires an external power source,such as a battery or DC supply,and is crucial for enhancing signal gain while minimizing noise,especially in low-signal environments.
By amplifying weak signals prior to reaching the receiver, active antennas substantially improve system performance, making them essential for long-distance communication, satellite systems, and scenarios where signal degradation is a concern.
The integration of an LNA endows active antennas with heightened sensitivity and superior signal-to-noise ratios, ensuring reliable reception even in challenging conditions.
Maxtena’s active antennas are celebrated for their high gain and low noise features, making them ideal for applications in UAVs, UGVs, IoT, smart cities, asset tracking, and automotive sectors.
For instance, the M10HCT-A-TNC active GNSS antenna provides up to 35 dB of gain with a noise figure of just 1.3 dB, ensuring robust communication even in areas with limited signal availability.
Exploring Passive Antennas
passive antennas are commonly utilized in various applications,including television and radio systems,due to their simple design and effectiveness in environments with sufficient signal strength.
These antennas do not need an external power source; instead, they capture electromagnetic waves from their surroundings and convert them into electrical signals for connected devices. Their straightforward construction makes passive antennas both cost-effective and efficient for scenarios where signal amplification is not required.
Maxtena offers a wide range of passive antennas tailored for diverse applications. The M1575HCT-22P-SMA helical L1 passive GPS antenna stands out as a reliable and durable option for GPS applications, delivering a gain of up to 22 dBi and a VSWR of 1.5:1, ensuring accurate positioning and timing.
Active vs. passive Antennas: A Comparative Analysis
The primary distinction between passive and active antennas lies in their approach to signal amplification. Passive antennas depend solely on capturing ambient electromagnetic waves,while active antennas are equipped with an LNA to amplify weak signals.
This amplification necessitates an external power source, allowing active antennas to excel in low-signal situations, thereby enhancing performance in long-range or weak-signal environments.
Active Antennas in GNSS Applications
In the realm of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) applications, active antennas are typically favored over passive ones for several reasons:
Amplification of Weak Signals
GNSS satellites orbit at considerable distances (around 20,000 km from Earth), resulting in weak signals by the time they reach terrestrial receivers.
Active antennas, equipped with an LNA, amplify these faint signals before they reach the receiver, ensuring a stronger and more usable output. In contrast, passive antennas rely solely on capturing the signal, which may be insufficient for effective processing.
Enhanced Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
The inclusion of an LNA in active antennas improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by amplifying the desired signal while minimizing noise. This leads to better performance, increased accuracy, and more reliable satellite tracking for GNSS receivers, which is crucial for applications requiring precise positioning.
Mitigating Cable Length Loss
In manny GNSS setups, antennas are placed away from the receiver, such as on vehicle rooftops or in outdoor locations. With passive antennas, long cable runs can result in signal degradation. Though, active antennas counteract this loss by amplifying the signal before it travels through the cable, thus reducing the effects of attenuation.
When to Consider Passive Antennas
In certain scenarios, a passive antenna may be a viable option for GNSS applications:
- When signal strength is adequate, such as in environments with minimal interference.
- When the antenna is situated close to the receiver,minimizing signal loss due to cable length.
Nonetheless, in most GNSS applications, especially where signals are weak or cable distances are extensive, an active antenna remains the more reliable and effective choice for ensuring strong signal reception and accuracy.
Read the original article >>