Knight Optical has published an insightful piece detailing the role of optical components in collaborative robots, commonly known as cobots. the article elaborates on the definition of a cobot, differentiates it from traditional robots, and explores its applications.
Looking back through history, we can identify various systems that share characteristics with modern robots. The origins of robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be traced back to ancient civilizations. As an example, the ingenious Ancient Greeks developed intricate automated puppet shows (1), while the Ancient Egyptians created mechanical systems embodied in figurines (2). Fast-forwarding to today, we see remarkable advancements since those ancient times, yet the core mechanics of some modern technologies echo those of the past.
A notable aspect of these early ‘robots’ is their capacity to replicate human actions, expressions, and behaviors, aimed at assisting us. as technology has evolved, the imitation by these machines has become increasingly refined, with some even engaging in conversation like humans. While many of these machines are large industrial entities confined to secure areas, a new trend has emerged where humans and robots work together as partners, referred to as cobots.
Understanding Cobots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are designed to work alongside humans to accomplish tasks. By partnering with human workers, cobots enhance efficiency and speed in task completion, while also reducing errors typically associated with human oversight, thus streamlining operations for businesses.
Distinguishing Between Robots and Cobots
Beyond the previously mentioned distinction, where traditional industrial robots operate behind barriers to ensure human safety, cobots and robots differ in their levels of autonomy.
As an example, conventional robots are often programmed for independent operation, executing a defined set of tasks in a controlled environment. In contrast, cobots are designed to be more adaptable and responsive to their surroundings. Equipped with sensors, they can detect human presence and modify their actions accordingly. For example, if a human approaches a cobot during operation, the cobot may slow down or halt to prevent collisions.
Another key difference lies in their complexity. Traditional robots can be highly specialized, requiring extensive technical knowledge for programming and operation. Conversely, cobots are designed to be user-kind, making them accessible to a wider range of users.
the primary difference between robots and cobots is that robots are typically built for independent operation, while cobots are intended to collaborate with human workers in shared environments.
Applications of cobots Across Industries
Due to their numerous advantages and growing versatility, cobots are being embraced by various industries worldwide.
Key sectors include:
- Manufacturing: for repetitive or hazardous tasks such as assembly, painting, and packaging.
- Healthcare: for dispensing medications and delivering supplies to patients.
- Agriculture: for activities like harvesting, planting, and spraying.
- Logistics: for tasks such as palletizing, sorting, and transporting goods.
- Food and Beverage: for packaging, quality assurance, and mixing.
- Retail: for restocking shelves and assisting customers.
- Construction: for tasks like bricklaying and painting.
The Future Landscape of cobots
As reported by IDTechEx, the adoption of cobots is anticipated to surge in the material handling and automotive sectors (3). The technology firm notes that many automotive manufacturers are shifting towards cobots to mitigate the costly downtime associated with traditional robots. According to their research, “An automotive manufacturer’s downtime cost per hour could exceed US $2 million per factory.” cobots present an chance for these companies to reduce downtime and enable safer, side-by-side operations in a more compact and flexible manner.
Real-World Implementation
Recent reports from 2023 highlight the extensive use of cobots in manufacturing environments. A notable example involves cobots being utilized for repetitive screw-driving tasks. Catherine Leclerc from Robotiq Inc,a company specializing in cobot solutions,shared insights with Assembly magazine,emphasizing that cobots have become essential in this sector due to labor shortages and high employee turnover (4).She explained how cobots allow manufacturers to implement automation solutions without requiring excessive space on the production line.
The trend of cobot adoption is further illustrated by a recent collaboration between two leading robotics firms. Rapid Robotics and Universal Robots (UR) are joining forces to enhance the deployment of cobots for North American clients. UR, a Danish manufacturer of collaborative robots, will provide Rapid Robotics with robotic arms to create cobot work cells. This partnership aims to combine UR’s rapid shipping capabilities with Rapid Robotics’ advanced AI and vision systems, paving the way for a promising future of high-performance cobots.
The Role of Optical Components in Cobots
Optical components are crucial for the effective functioning of modern cobots, enabling them to perceive and react to their surroundings in real-time, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Optics serve several essential functions, including:
- Cameras: provide visual feedback to the control system, allowing it to perceive and respond to its environment. They are also utilized for quality control and inspection tasks.
-
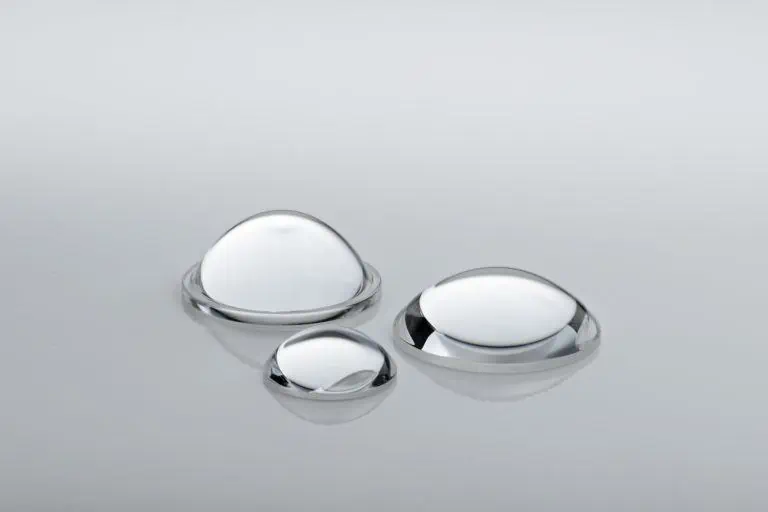
Lenses:
focus light and are found in cameras, laser sensors, and other optical systems within cobots. Different lens types are employed based on the specific application of the cobot.
- Laser Sensors: utilize laser beams to measure distance,position,or shape of objects in the cobot’s environment,frequently enough used for precision positioning and navigation.
- Light Curtains: create a series of light beams that detect when an object or person enters a designated area, commonly used as a safety feature to prevent collisions with humans.
- Projectors: display visual information, such as work instructions or safety alerts, to the cobot operator.
Why Choose Knight Optical for Your needs?
Customers trust Knight Optical not only for the exceptional quality of our products and the capabilities of our state-of-the-art Metrology Laboratory and QA Department but also for our range of Stock Optics available for next-day dispatch, as well as our Custom-Made Components.
With over thirty years of experience and a portfolio of long-standing, renowned clients, we take pride in having contributed to some of the most innovative advancements in the field.
FOOTNOTES
(1) https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-018-05773-y
(2) https://egyptindependent.com/ancient-egyptians-invented-first-robot-4000-years-ago-study/
(3) https://www.idtechex.com/en/research-article/cobots-on-the-rise-for-the-automotive-and-material-handling-industries/28754
(4) https://www.assemblymag.com/articles/97577-screwdriving-with-cobots