This article explores the Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool introduced in Global Mapper Pro v25, focusing on point cloud classification, innovative automatic classification techniques, and the extraction of vector features.
In the latest version, Global Mapper Pro v25, the Automated Point Cloud Analysis Tool has taken the place of the previous Lidar Analysis toolbar, serving as the central interface for point cloud classification, segmentation, and extraction. This new interface allows users to select layers for processing, apply filters, open tools in tabs within the same or adjacent panes, and manage feature models for classification.
Users familiar wiht earlier versions of
Global Mapper
will notice a significant redesign in the classification, segmentation, and extraction tools. The former Automatic Point cloud toolbar has been removed, but rest assured, all yoru preferred tools and settings remain accessible. These functionalities have been consolidated into a single dialog, enabling shared settings and the capability to execute multiple classifications at once. This unified interface is known as the
Automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool
.
In the past, processing a point cloud involved multiple steps, requiring users to open each tool separately and set parameters like bounds and resolution.The Automatic Point cloud Analysis tool streamlines this process by integrating all necessary tools into one window, allowing for shared settings across classifications and extractions.
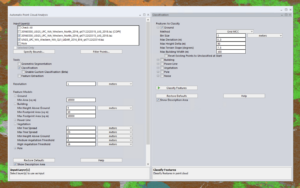
Classification, segmentation, and extraction tools are now centralized in the automatic Point Cloud Analysis tool.
Custom Classification Training Feature
The segmentation tool is invaluable for dynamically classifying points based on their existing attributes.Imagine being able to train Global Mapper to identify similar features in various point clouds. The existing automatic classification tools in Global Mapper cover commonly classified structures like ground, buildings, and poles. The new Custom Feature tool allows users to define unique classifications based on user-generated training samples, enabling the creation of automatic point cloud classifications tailored to specific objects in your data.
Segmentation identifies objects within a point cloud by analyzing the attributes and structure of the points. For instance, to segment road markings, you would search for points that form a flat surface and share similar color attributes. This method operates on the premise that each “object” in the point cloud,or cluster of points,possesses a unique signature made up of attributes and/or structures that distinguish it from neighboring points. The new Custom Feature Template tool leverages these signatures, allowing users to train a custom classification tool to detect specific signatures within the point cloud.

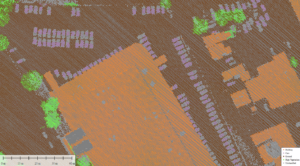
This segmented point cloud separates individual vehicles from surrounding data points. These vehicle points were utilized to train a new automatic classification tool for vehicle identification.
Point Cloud Classification Techniques

The Classification tool features familiar settings along with new classification methods.
When the Automatic Point Clouds Analysis tool is launched, classification is activated by default. All automatic classification methods from earlier versions are now accessible within a single window. Previously,each method required its own tool with distinct settings that needed to be executed in sequence. Now, users can select one or multiple classifications, and Global Mapper will process them in a predetermined order based on the selected methods.The standard sequence is noise, ground, building, vegetation, powerline, and pole.Remember to check the additional shared settings in the point Cloud Analysis window.
Innovative Automatic Classification Techniques
Users familiar with earlier versions may recall the “Non-Ground” classification tool for buildings and vegetation, which utilized two distinct analysis methods: Gridding and Segmentation. This concept has now been expanded to include ground and noise classifications. Users can select a method for each class from the drop-down menus.
gridding,
also known as MCC (Multiscale Curvature Classification),is the original method designed for data primarily collected by fixed-wing aircraft. This method has largely been replaced by the Max Likelihood method, which is more suitable for data gathered through various means. For data collected using methods other than fixed-wing aircraft, the Max likelihood method is recommended.
Max Likelihood
is a segmentation technique tailored to identify common shapes and characteristics of features within the point cloud. While this method offers fewer settings than the grid methods, users can further refine their point cloud settings using the Custom Classification tool. When activated, this tool allows users to train the automatic classifications. Refer to the Custom Classification Training section below for more details.
Tip: The undo functionality is also applicable to classifications. Use (ctrl z) to reverse recent actions.
Geometric Segmentation
Segmentation
is a distinctive and powerful feature of Global Mapper. This user-guided, automatic tool divides the point cloud into smaller segments based on the spatial and attribute relationships among points. It identifies objects by examining the attributes and structure of the points. Such as, to segment road markings, you would look for points that form a flat surface and share similar color attributes.By breaking down a point cloud into smaller sections,users can more effectively select clusters of points for manual classification or to train a custom classification.
For a practical example, check out this blog that demonstrates the use of segmentation to classify
transmission towers
. The segmentation settings from the previous dialog are transferable to the new interface and can be utilized to train a custom classification tool.
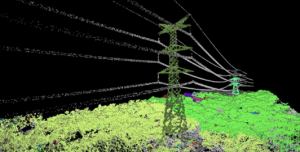
Segmentation helps identify clusters of points that form an object, such as these towers.
extracting Vector Features
Once a point cloud has been classified, features can be extracted as 3D point, line, or area features using the
Feature Extraction
tool. This is where the shared Feature model settings prove beneficial. The settings used for classifying features will also apply during extraction. Extracted layers will retain many attributes from the original features, such as height, elevation, or canopy width. A new enhancement in this tool includes an improved method for measuring tree canopy areas and the introduction of new 3D mesh features to estimate tree canopy structures.

The building features in this airport were extracted from a classified point cloud.
Experience Global Mapper Pro with a
free 14-day trial
today. For any inquiries,please
contact us.
























