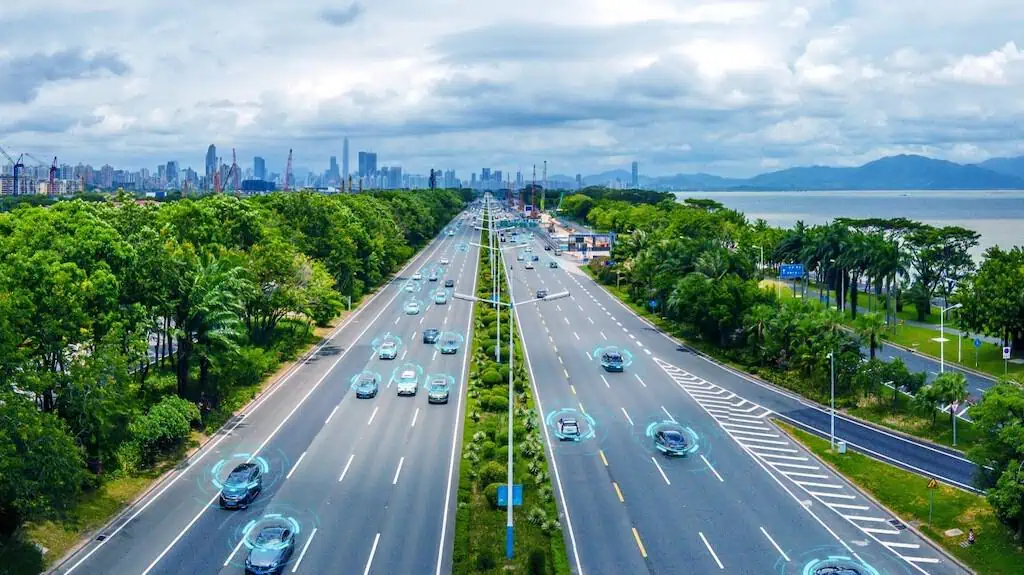
CHC Navigation explores the automotive sectorS current landscape, poised for a significant shift due to the swift evolution of self-driving technologies. Discover more >>
By 2026, the autonomous vehicle (AV) market is anticipated to soar to $557 billion, showcasing its vast potential. Over 500 firms globally are engaged in the progress of AV technologies,with major contributors located in the United States,China,and Germany. The number of AVs on the roads is projected to increase from 8.5 million in 2019 to more than 20 million by 2030.
A pivotal advancement in this journey is the rollout of Level 3 (L3) autonomous driving, which allows for hands-free operation under certain conditions. By 2024, top automotive manufacturers are set to introduce L3 features in their flagship models, while regulatory bodies in North America, europe, and Asia are evolving to support these innovations.
As AV technology progresses, the necessity for accurate positioning and navigation systems, especially GNSS+INS solutions, is becoming increasingly critical.

The Advancement of Autonomous Driving and the imperative for Precision
Self-driving vehicles depend on a complex combination of computing power, artificial intelligence, and sensor technologies to navigate safely. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) categorizes automation into six levels, from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation).
At present, the majority of AVs function at Level 2 (L2), where systems like Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) facilitate lane-keeping and adaptive cruise control. While these features enhance highway driving, they still require constant driver oversight. In contrast, L3 automation signifies a transition to conditional autonomy, allowing vehicles to perform most driving tasks independently, thereby substantially alleviating the driver’s responsibilities.
To achieve higher levels of automation, robust environmental perception and ultra-precise positioning are essential. this is where GNSS and inertial navigation systems (INS) become vital, supplying the foundational data necessary for dependable autonomous navigation.
GNSS and INS: A Synergistic Approach to Autonomous Navigation
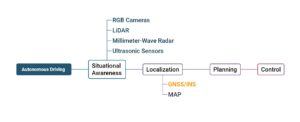
Self-driving vehicles rely on a network of sensors to understand their habitat and pinpoint their exact location. This ecosystem comprises:
-
Situational awareness Sensors:
-
RGB Cameras: Capturing visual details for object identification
-
LiDAR: Creating detailed 3D representations of the surroundings
-
Millimeter-Wave Radar: Measuring object speed and distance
-
Ultrasonic Sensors: Assisting in short-range obstacle detection
-
-
Positioning and Navigation:
-
GNSS/INS Systems: Providing accurate location and timing data crucial for autonomous decision-making
-
The integration of GNSS and INS is particularly vital, ensuring uninterrupted positioning even in challenging scenarios such as urban settings, tunnels, and underpasses. GNSS offers absolute positioning through satellite signals, while INS employs accelerometers and gyroscopes to monitor movement, compensating for data gaps when GNSS signals are weak or obstructed.
Addressing Challenges: The Importance of Tightly Coupled GNSS+INS Systems
Unlike conventional GNSS receivers used in surveying, those tailored for autonomous vehicles must adhere to rigorous standards:
-
Centimeter-Level Precision: Accurate lane positioning is essential. However, urban landscapes can obstruct GNSS signals and introduce multipath interference, compromising accuracy.
-
Environmental Resilience: AVs function in diverse conditions, necessitating GNSS receivers that can endure vibrations, temperature variations, and signal disruptions.
-
Real-Time Processing: Autonomous navigation requires continuous, low-latency positioning updates, even in GNSS-compromised environments.
Tightly coupled GNSS+INS systems tackle these challenges by integrating raw GNSS and INS data at an early processing stage, rather than merging outputs separately. This approach allows the system to maintain accuracy even during GNSS outages, as the INS component continues to deliver reliable navigation data.
CHCNAV’s Cutting-Edge GNSS+INS Solutions for Autonomous Vehicles
CHCNAV has introduced a series of high-precision GNSS+INS sensors aimed at enhancing navigation for autonomous vehicles. The CGI-610 GNSS/INS sensor, such as, offers:
-
Centimeter-Level Precision: Ensuring accurate localization for AV operations
-
Multi-Constellation Support: Enhancing reliability in urban settings
-
Advanced Algorithms: Facilitating rapid initialization and re-convergence
-
Robust Durability: Engineered to function in extreme conditions, including high-vibration environments
Field Testing: Demonstrating Performance in Real-World Scenarios
To assess the CGI-610’s capabilities, CHCNAV conducted extensive field trials in intricate urban settings in Japan. Mounted on a light truck and linked to an external antenna and GNSS RTK correction network, the system was evaluated under various conditions:
-
Urban Business Districts: Achieved RMS positioning accuracy within 0.7m, with heading accuracy around 0.1°
-
Open Roads: Reached sub-0.1m RMS accuracy, ideal for AV lane positioning
-
Dense Urban Areas: Maintained positioning accuracy within 0.5-1m RMS despite signal interference
-
Tunnels: Positioning errors remained within 1.5% of tunnel length, with RMS values under 0.5m
These findings confirm that the CGI-610 provides dependable positioning and heading accuracy, even in environments with significant GNSS signal challenges.
The Future: Advancing GNSS+INS Technology
As the autonomous driving sector evolves, the need for highly accurate GNSS+INS solutions will continue to escalate. Future advancements may incorporate AI-driven sensor fusion, enhanced real-time corrections, and improved energy efficiency to extend operational longevity.

CHCNAV is leading the charge in these advancements, with next-generation receivers like the CGI-830 and CGI-230 building on the success of the CGI-610. These systems provide enhanced INS accuracy and superior positioning performance, ensuring that autonomous vehicles navigate with the precision necessary for safe and efficient operation.
By refining GNSS+INS technology, CHCNAV is paving the way for the widespread integration of autonomous vehicles, ensuring that precise navigation remains a essential aspect of the industry’s future.
read the original article, or visit the CHCNAV website.