EIZO has published an insightful article detailing how NVIDIA’s Ampere architecture enhances its embedded systems, catering to both conventional rendering tasks and GPGPU functions, including target detection through traditional and AI/ML methodologies.
In the realm of autonomous vehicles, particularly UAVs, the demand for highly efficient computing systems is paramount. These systems must deliver precise vision and perception capabilities within SWaP (Size, Weight, and Power) constraints, all while maintaining optimal performance. high-Performance Computing (HPC) systems deployed at the edge require robust GPGPU processing hardware to ensure that advanced Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms can operate effectively within their designated workflows.
Crucially, the technology employed in mission-critical scenarios can be a matter of life and death. The computer systems responsible for sensor analysis and complex mathematical computations must achieve exceptional accuracy to guarantee the safety and success of operations. AI and ML runtimes utilized in radar tracking, weapon systems, and ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) operations necessitate optimized hardware to ensure that precision is achieved promptly.
NVIDIA’s Ampere architecture offers numerous advantages for embedded systems, delivering significant performance enhancements in both traditional rendering and GPGPU tasks, such as target detection through conventional and AI/ML techniques. With its enhanced support for “AI at the Edge,” this technology elevates computing power for data-centric applications.
the Ampere architecture incorporates cutting-edge high-speed graphics memory, GDDR6 with Error Correction Code (ECC).This ECC memory ensures data integrity and reliability, which is particularly beneficial for SIG-INT, Electronic Warfare, and various digital signal processing applications.
The introduction of third-generation Tensor Cores advances deep learning matrix operations, facilitating neural network training and accelerating AI inference, enabling even the most intricate models to be processed at the edge. These new cores provide a performance boost of 2-3 times compared to the previous Turing generation.furthermore, the Ampere Tensor Cores support the innovative hybrid Tensor Float 32 (TF32) data type, which expands the numerical range of FP32 while maintaining the efficiency of FP16. This combination, along with base improvements and a new sparsity feature, can yield a processing throughput increase of 10-20 times for AI/ML models compared to earlier tensor cores, all without necessitating changes to the underlying software.
With up to double the throughput of its predecessor and the capability to together execute ray tracing alongside shading or denoising tasks, the second-generation RT cores provide substantial speed enhancements for real-time rendering. this technology also accelerates the rendering of ray-traced motion blur, resulting in quicker outcomes with enhanced visual fidelity, which could significantly impact simulation and radar processing sectors.
Thanks to advancements in both RT Cores and Tensor Cores, Ampere GPUs present an optimal solution for demanding AI-accelerated applications, including raw video rendering and streaming, image analysis, object tracking, and motion detection. Additionally, the Ampere architecture boasts a remarkable 2-3 times improvement in power efficiency per watt for its base streaming multiprocessor, making its CUDA cores twice as power-efficient compared to the previous Turing GPUs.
PCIe Gen 4 – Doubling the Bandwidth
The Ampere GPU lineup is the first to embrace PCI express Gen 4, which offers double the bandwidth compared to PCIe 3.0. PCIe Gen 4 can achieve up to 16 Gigatransfers per second, with a x16 PCIe 4.0 slot providing a peak bandwidth of 32 GB/sec. This increased bandwidth enables users to fully leverage the processing speeds of the latest architecture.
PCIe Gen 4 enhances data transfer rates from CPU systems that support Gen 4, ensuring that the transfer bus does not bottleneck data-intensive operations such as graphics rendering, AI/ML tasks, data science, and other image/sensor analyses.RDMA (Remote direct Memory Access) utilizing NVIDIA GPUDirect further mitigates bottlenecks caused by CPU memory inefficiencies, allowing other RDMA-enabled devices to transfer data directly to GPU memory, thereby maximizing the potential of the PCIe Gen 4 bus. This results in a powerful graphics and AI processing solution for mission-critical applications, with both the processor and bus capable of managing the substantial data generated by edge hardware.
The integration of PCIe Gen 4 is particularly crucial for embedded systems in the defense sector, as the newly released Revision 1.0 of the Sensor open Systems Architecture (SOSA) technical standard introduces profiles that mandate Gen 4 PCIe for SOSA-compliant HPEC systems.
openvpx Hardware Featuring Ampere GPU
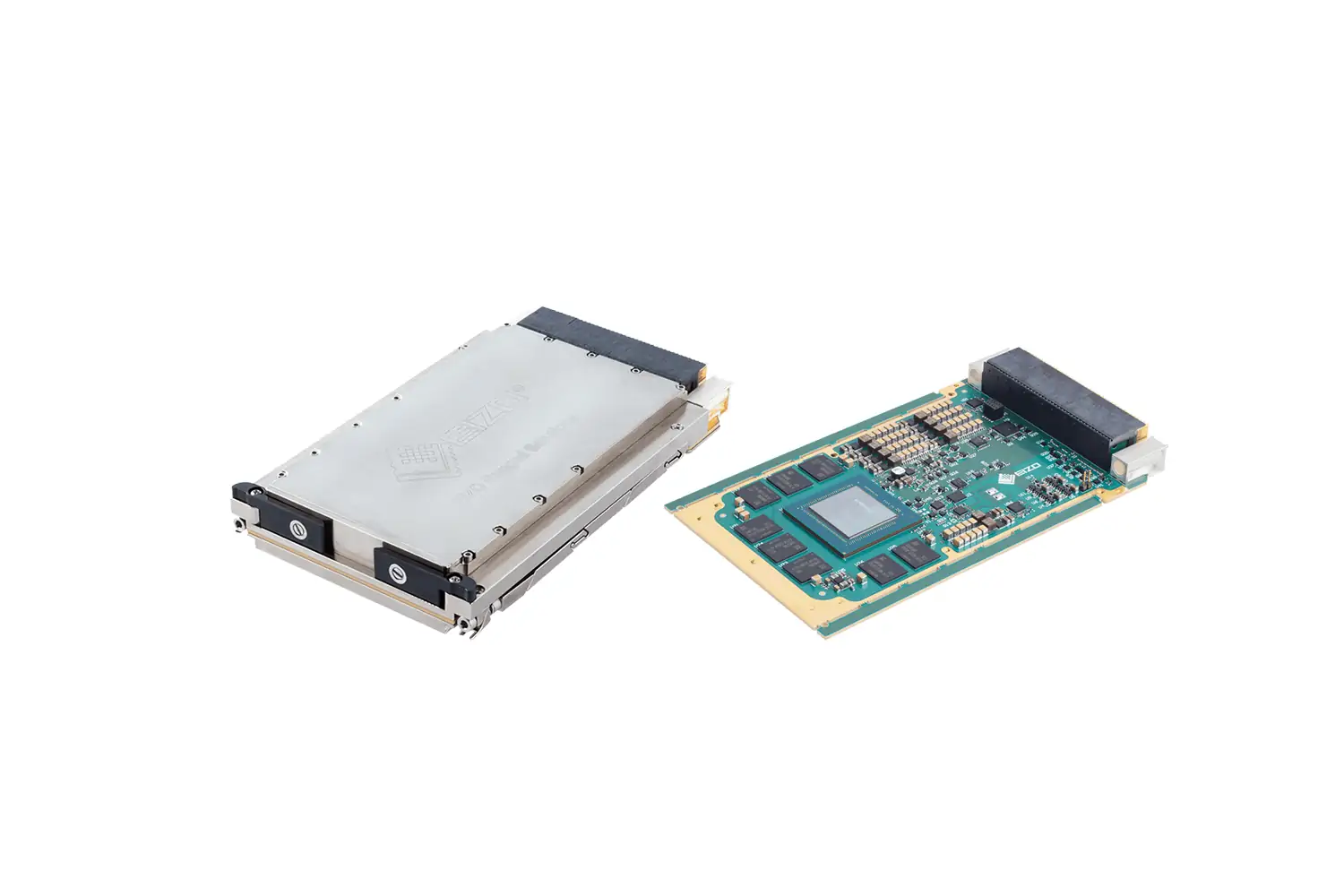
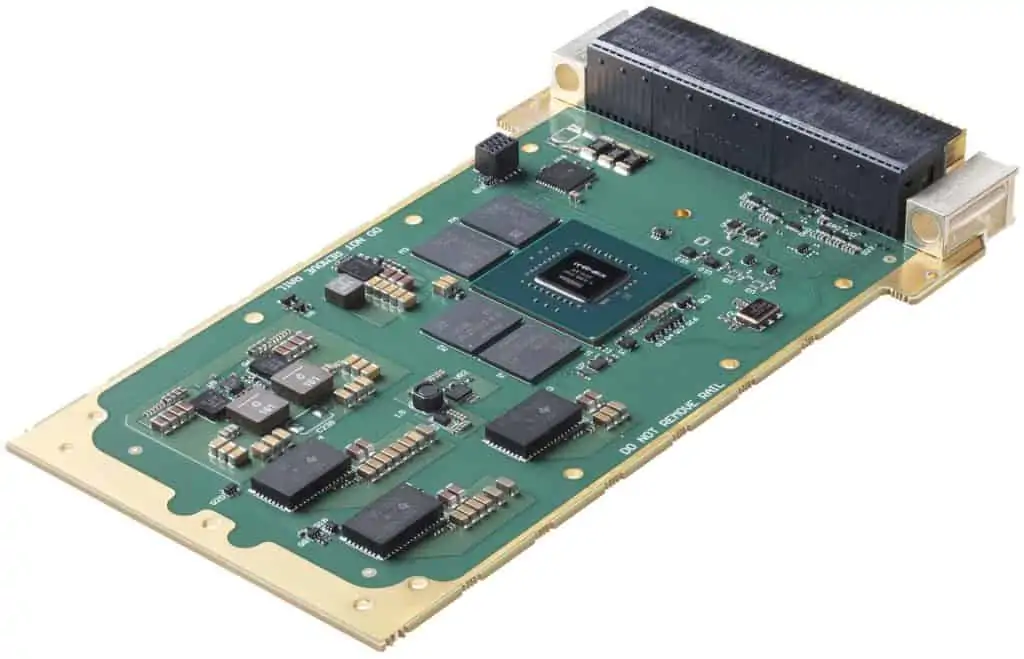
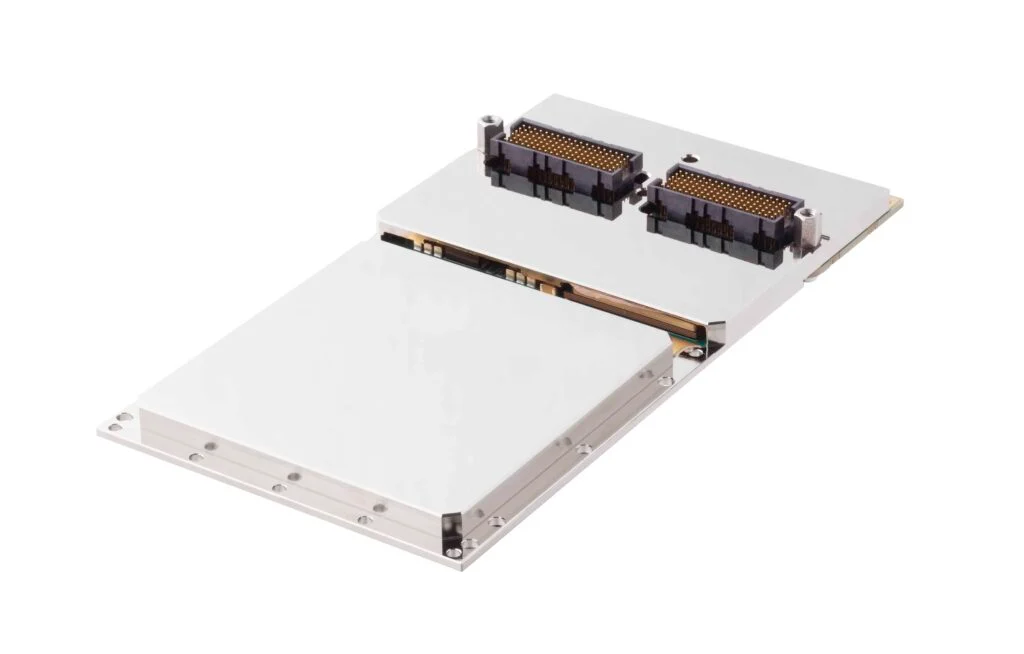
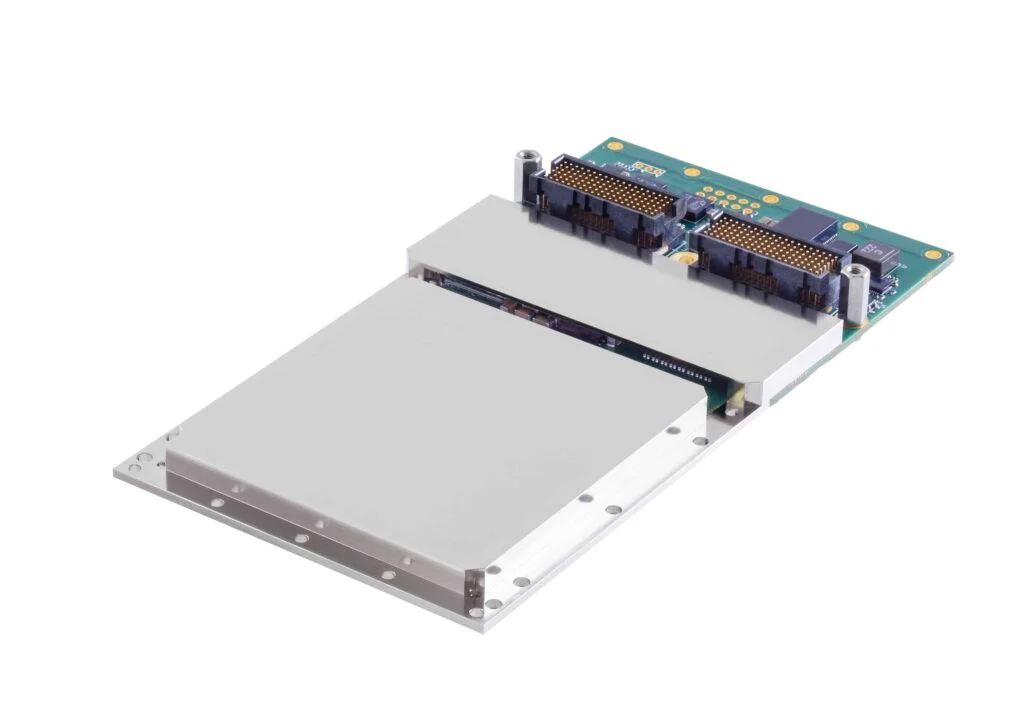
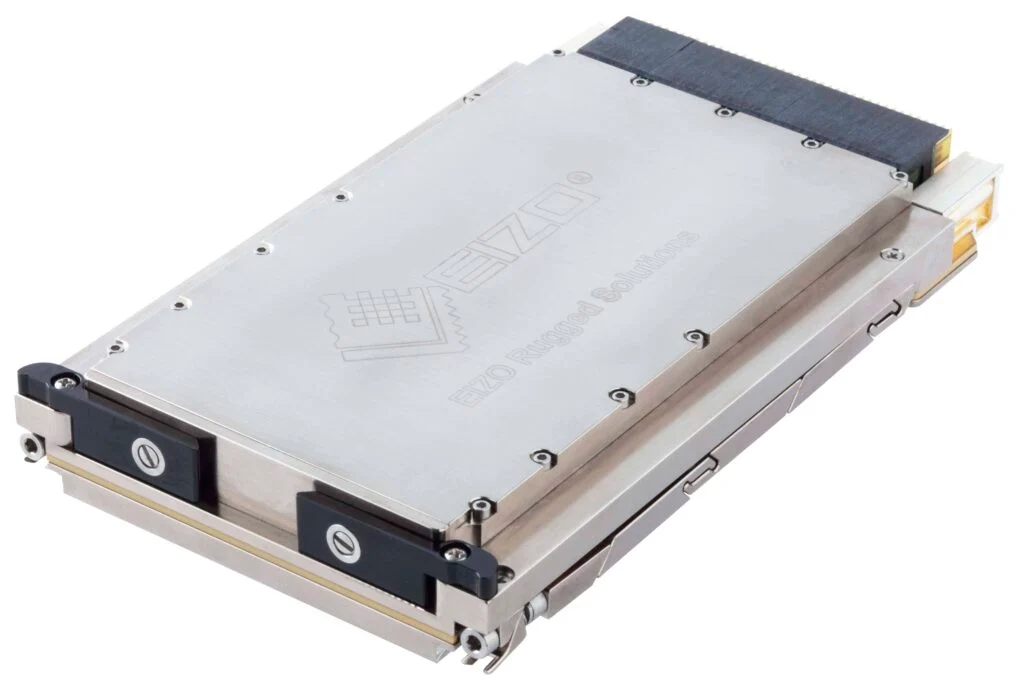
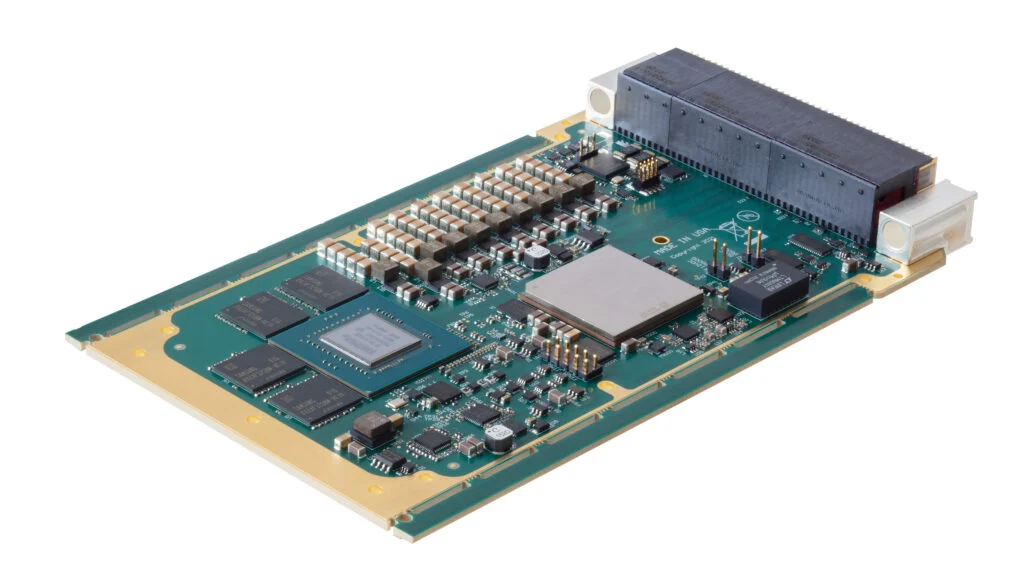
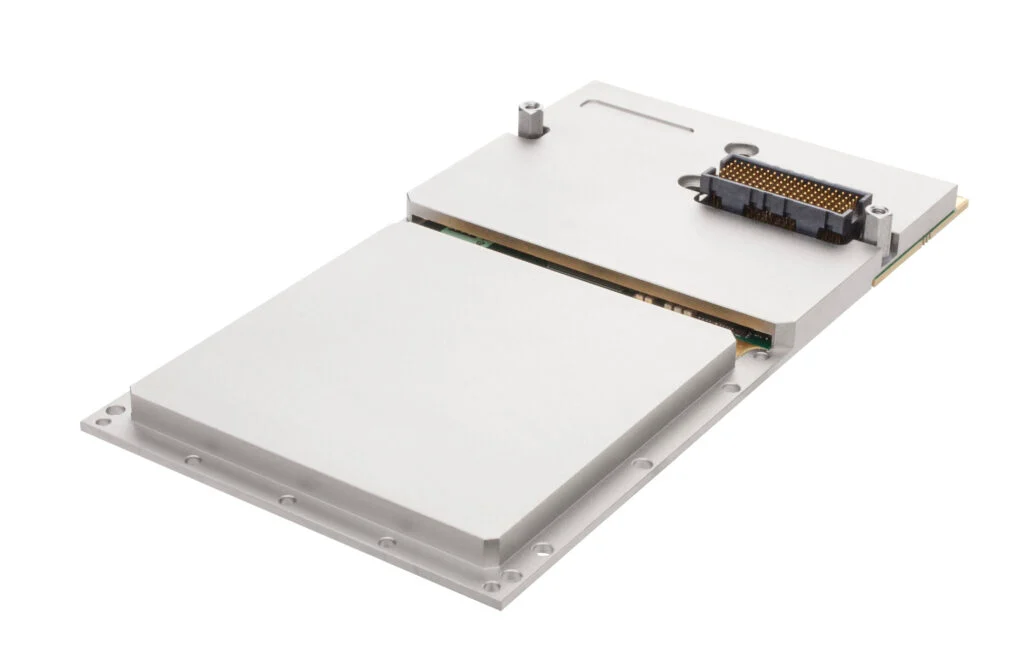
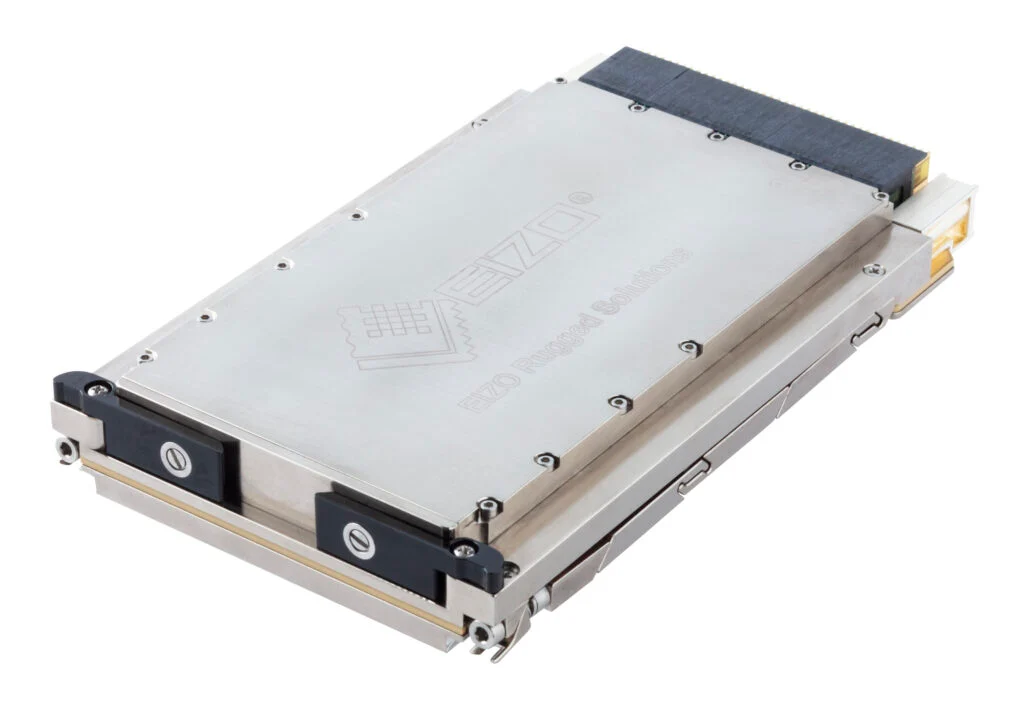
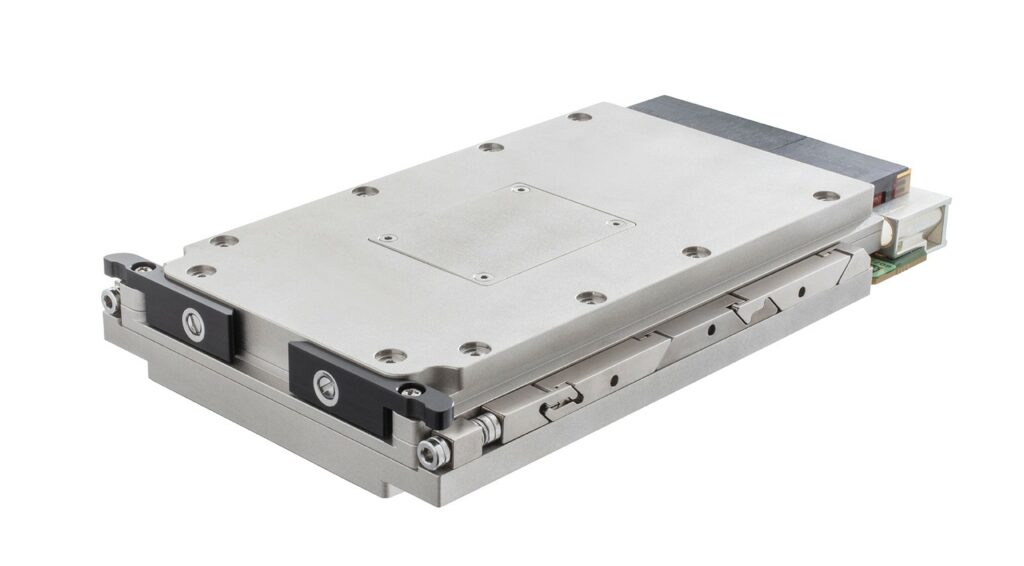
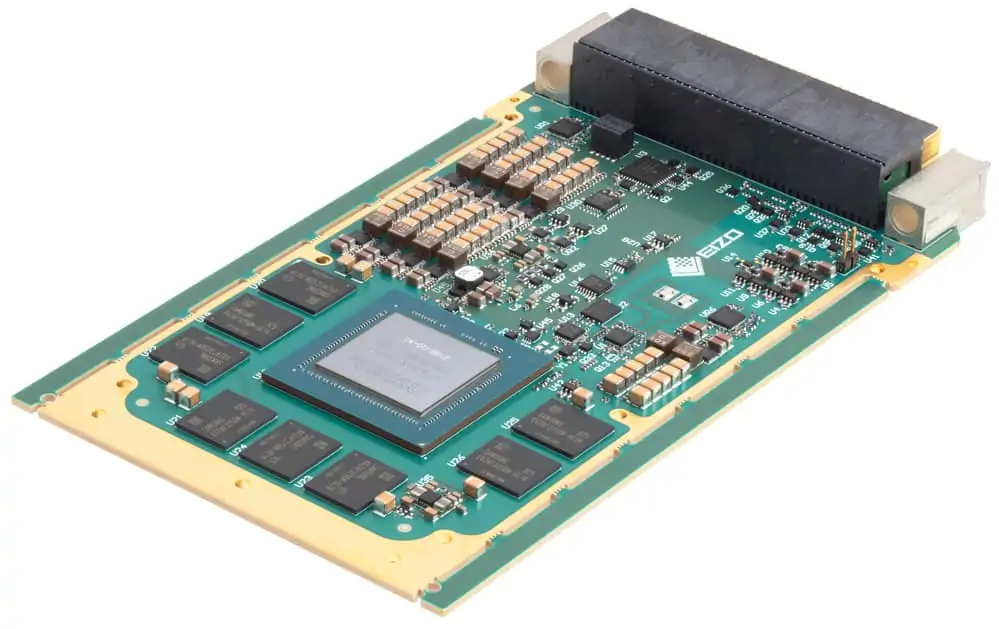
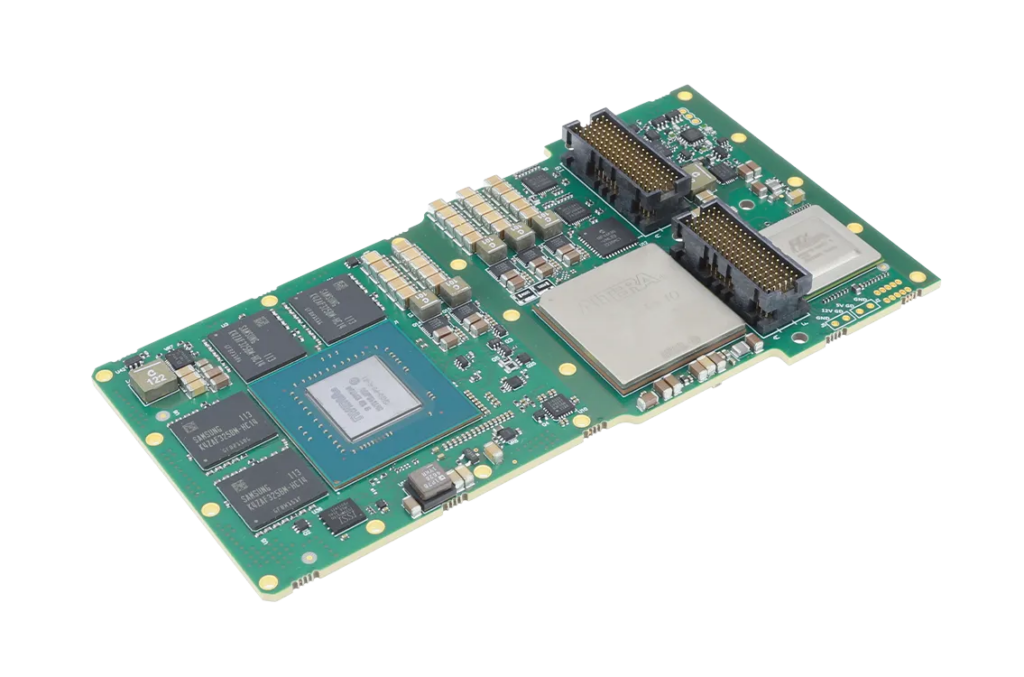
EIZO leads the market with its rugged Ampere-based OpenVPX 3U form factor HPC graphics and GPGPU card.The Condor GR5-A2000 is an embedded 3U VPX HPEC graphics and AI-enabled GPGPU card powered by the energy-efficient NVIDIA ampere RTX A2000 GPU. This embedded GPU variant is equipped with 2560 NVIDIA CUDA Cores, 20 RT cores, and 80 Tensor Cores, along with top-tier H.265 (HEVC) / H.264 (MPEG4/AVC) encoding and decoding engines.
The Condor GR5-A2000 supports traditional DisplayPort and Single-Link DVI outputs, as well as 2x 3G-SDI displays for integration in the most demanding environments.It is the first GPU on the market to support PCIe Gen 4, unlocking the full potential of newer generation CPU and payload cards while maintaining a SWaP-optimized maximum power footprint of 70W, with configurability options to reduce clocking for lower power consumption.