Tyto Robotics explores the mechanics of Distributed Electric Propulsion (DEP),it’s advantages and disadvantages,notable DEP aircraft,and a method for evaluating DEP systems.

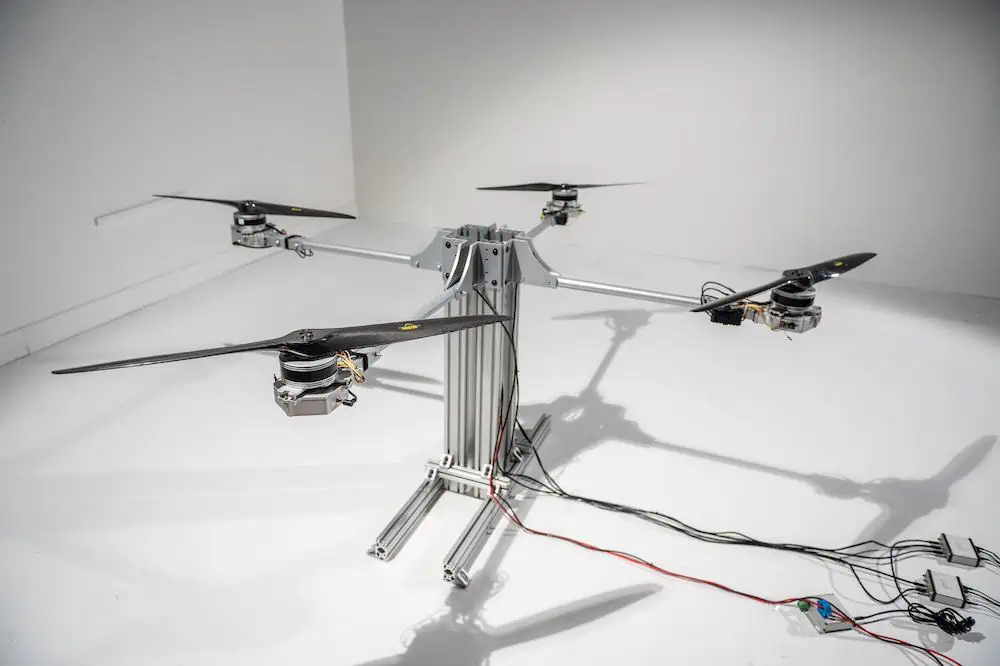
Design of a fully electric DEP aircraft.
Distributed Electric Propulsion (DEP) was developed to enhance the capabilities of contemporary aircraft. The key questions it seeks to answer include: How can we boost an aircraft’s efficiency? Enhance its agility? Reduce the distances required for take-off and landing?
DEP technologies hold the promise of decreasing fuel usage while together enhancing performance, a compelling prospect as the aviation industry strives for greater sustainability.
At its core, Distributed Electric Propulsion refers to a system where thrust is generated by three or more electric propulsors. Typically, these electric propulsors—whether fans or propellers—are arranged in parallel along an aerodynamic surface, such as an aircraft’s wing.
DEP systems can be categorized as either fully electric, powered by batteries, or hybrid, where electric motors draw energy from a turbogenerator.
numerous prominent organizations,including NASA,are actively engaged in developing and testing various DEP designs.
Currently, there is no universally accepted definition of DEP, other than the essential requirement of multiple electric propulsors.
As an evolving concept, DEP aircraft vary substantially in design. However, they generally fall into two primary categories: fully electric DEP aircraft and hybrid turboelectric DEP aircraft.
Notable examples of fully electric DEP aircraft include the Lilium Jet, NASA’s revamped X-57 Maxwell, and the Airbus Vahana.
Challenges associated wiht Distributed Electric Propulsion include:
- Integration and complexity
- Redesigning conventional components
- Scalability and power demands
Evaluating a Distributed Electric Propulsion System
Given the intricate nature of DEP systems, thorough testing is crucial for safe development.But what methods are available for testing a DEP system?
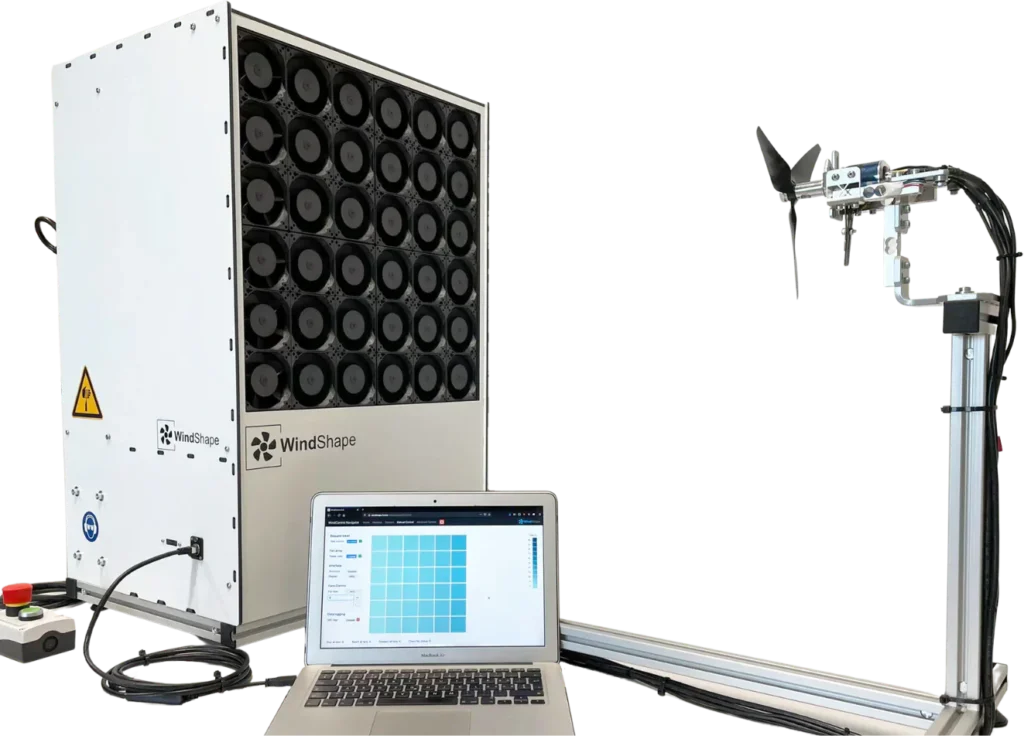
Tyto Robotics has created a testing platform capable of evaluating distributed electric propulsion systems with up to eight powertrains. This platform includes the necessary hardware, software, and electronics to simultaneously assess the performance of eight motors and propellers.
Testing platform for distributed electric propulsion.
The platform’s hardware and electronics utilize a combination of load cells and sensors to measure thrust, torque, RPM, voltage, current, temperature, and power of the propulsion system.
These metrics are essential for calculating motor and ESC efficiency, propeller performance, and overall efficiency for individual powertrains or a combination of up to eight.
The testing software allows for manual, automatic, or python API programming of tests. Tyto robotics also provides a flight replay feature, enabling users to upload flight controller data into the software, using throttle points as a testing template.
Each powertrain can be identified and mapped for easy data tracking. With real-time live plots displaying incoming data,users can quickly assess the efficiency of different propulsors.
For the complete article, click here, or visit the tyto Robotics website for more details.