MKS-Ophir offers cutting-edge SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR zoom lenses that provide outstanding long-range detection, compact size, weight, and power (SWaP) optimization, along with compatibility with the latest small-pixel, large-format infrared (IR) detectors.
The role of infrared (IR) imaging technology is pivotal in contemporary security and surveillance frameworks, facilitating the detection, recognition, and identification (DRI) of objects across diverse environments.
Thes capabilities are essential for various applications, including intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR), targeting, border security, and counter-drone initiatives.
Even though IR imaging has been around for many years, its importance—and the intricacies involved in its implementation—have surged due to advancements in sensor technology, increasingly complex threats, and evolving market dynamics. Consequently, high-performance zoom lenses for IR cameras are now indispensable for capturing clear images of individuals, vehicles, drones, and other distant subjects.
This article delves into the complexities of designing and producing high-performance IR zoom lenses tailored for DRI applications. It highlights innovative solutions from MKS-Ophir that address these challenges and provides an overview of long-range product offerings in SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR, showcasing the current advancements in IR technology.
The SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR spectral ranges coexist, each providing unique benefits. SWIR is ideal for long-range daytime observation, while MWIR is superior for long-range surveillance in both day and night conditions.
Both MWIR and SWIR perform effectively in challenging environments, such as smoke, dust, heavy haze, and high humidity. Conversely, LWIR is the preferred range for observing burning targets and mitigating sun glints.
Essential Requirements and Trends in DRI
DRI applications necessitate highly specialized imaging systems to fulfill rigorous requirements and operate optimally in a variety of demanding conditions. However, the performance expectations for DRI are continually evolving due to several external influences.
Advancements in Sensor technology
Ongoing technological progress is yielding sensors with smaller pixel pitches and higher pixel counts,resulting in enhanced camera resolution. Consequently, designers of IR imagers must prevent “optics-limited” scenarios, where the performance of the imaging system is restricted by the optics rather than the sensor.
Currently,sensors with a 10 μm pixel pitch are standard,with even smaller sizes (8 μm,7.5 μm, or 5 μm) becoming increasingly common. The SXGA sensor format (1280 x 1024 pixels) is prevalent, with some systems utilizing full HD format (1920 x 1080 pixels) sensors.
SWaP-C Optimization
Optimizing size, weight, power, and cost (SWaP-C) is a primary concern in military system design, shaping the development of advanced technologies across various platforms. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones employed in DRI applications require optical systems that are lightweight, compact, and energy-efficient without compromising performance.
Multi-Spectral Imaging
Contemporary surveillance systems often employ multispectral imaging, functioning across multiple spectral bands (visible, SWIR, MWIR, and LWIR) to conduct effective surveillance under diverse lighting and weather conditions. This enhances situational awareness and improves the ability to detect, identify, and recognize elements and threats within a scene.
Environmental and Operational Challenges
Security and surveillance operations frequently occur in harsh environments, including extreme temperatures, rain, fog, dust, and exposure to saltwater.
Day-and-night operations are standard,and imagers may face shock,vibration,and require regular cleaning. Lens designs must withstand these operational challenges without sacrificing performance.
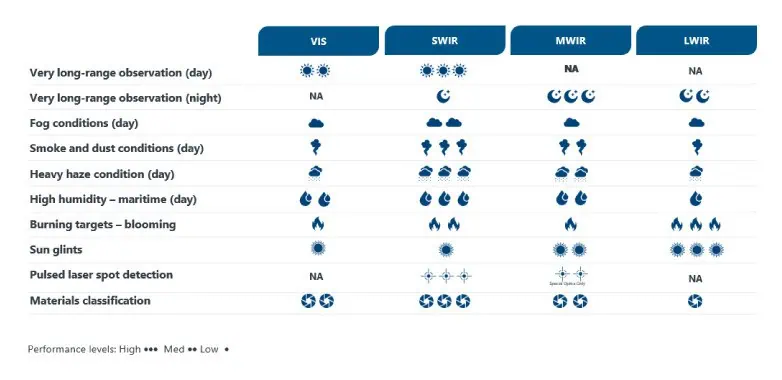
Table 1: Performance Comparison: SWIR vs MWIR vs LWIR
Innovative Solutions from MKS-Ophir
To meet the demands of modern security and surveillance operations, a specialized approach in both design and manufacturing is essential. MKS-Ophir employs various strategies to fulfill the high requirements for DRI and SWaP-C performance.
DRI Resolution Standards
MKS-Ophir’s advanced design capabilities cater to the stringent resolution and optical performance criteria for DRI lenses. The design process utilizes extensive expertise and cutting-edge optical design software to create innovative solutions.
Designers at MKS-ophir have access to a wide array of materials, surface shapes, and surface types, enabling the use of spheres, aspheric elements, freeforms, and even diffractive or holographic components to achieve high modulation transfer function (MTF) targets and minimize chromatic aberrations.
The production capabilities at MKS-Ophir are crucial for realizing the full potential of these designs. High-precision fabrication techniques ensure accurate optical surface production and precise component alignment. Utilizing large diameter optics, for instance, is beneficial for achieving high magnification in DRI zoom lenses.
Moreover, integrating design and manufacturing within a single facility allows MKS-Ophir to apply design for manufacturing (DFM) principles, promoting continuous improvement and performance optimization.
SWaP-C Optimization
By employing advanced IR materials, MKS-Ophir reduces the number of lens elements, thereby minimizing system size, weight, and production costs. Aspheric and diffractive elements help to reduce aberrations and the number of components, which is vital for compact continuous zoom lens designs. MKS-Ophir’s SWaP-C capabilities are further enhanced by utilizing folded-optics configurations and multi-spectral designs.
Durability and Environmental Stability
MKS-ophir lenses are often made from materials such as titanium and magnesium alloys,chosen for their strength,lightweight properties,and resistance to corrosion. Athermalization techniques ensure these lenses maintain focus across a wide temperature range.
Combining materials with different thermal expansion coefficients allows for the creation of assemblies that inherently compensate for thermal variations. Lenses that remain stable and accurate in fluctuating environmental conditions reduce the need for frequent recalibration, enhancing the operational efficiency of surveillance systems.
Hard carbon (HC / DLC) and high-durability (HD) coatings are applied to optical surfaces to resist abrasion and environmental degradation. MKS-Ophir lenses also meet or exceed IP67 environmental standards, ensuring reliable performance in rain, dust, and extreme conditions.
Production Capabilities
MKS-Ophir provides a thorough range of IR optics for security and surveillance applications, including:
- SWIR lenses
- MWIR lenses for cooled cameras
- LWIR lenses for uncooled cameras
- Lightweight IR zoom lenses
- Long-range IR zoom lenses
Product Overview
MKS-Ophir manufactures over one hundred IR zoom lenses, including more than a dozen specifically designed for DRI applications. Below are examples of products that showcase MKS-Ophir’s achievements in optimizing performance, weight, and size.
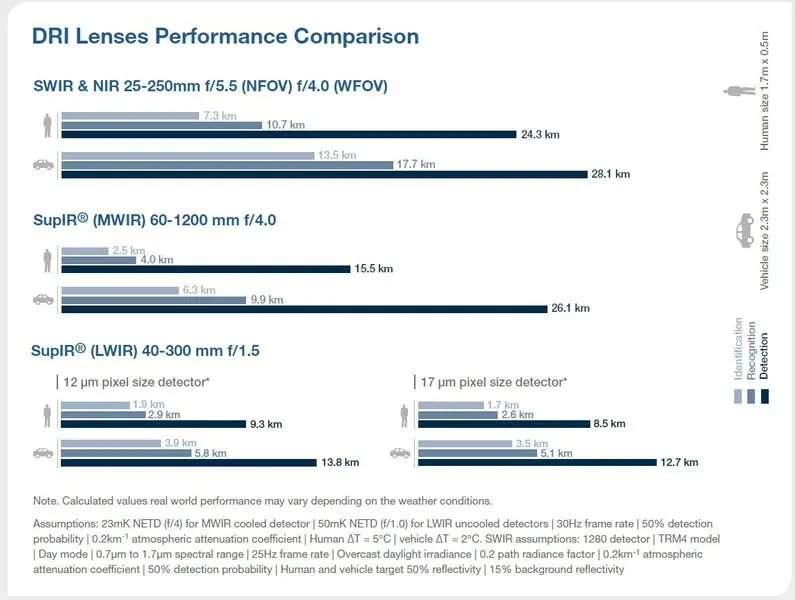
SWIR & NIR 25-250mm f/5.5 (NFOV) / f/4.0 (WFOV)
The SWIR & NIR 25-250mm f/5.5 lens combines a broad detection range with effective operation in various conditions,including both day and night. Its ability to penetrate haze, smoke, and maritime fog enhances its operational utility.
Designed for compatibility with the latest 5 μm SXGA SWIR detectors, as well as 10 μm SXGA and 15 μm VGA sensors, this lens signifies a major advancement in SWIR technology.
Notably, the lens is optimized for SWaP, achieving a weight of 0.86 kg and a length of 214 mm—approximately 60% lighter than comparable SWIR lenses. Additionally, chromatic correction extends usability down to 0.7 μm with minimal distortion.
Key Advantages
- Compatible with 12 μm pixel 1280×1024 SXGA uncooled LWIR cameras
- Passive athermalization for stable performance in various conditions
- Vehicle detection range exceeding 12.5 km
- High-durability, low-reflection hard-carbon AR coatings
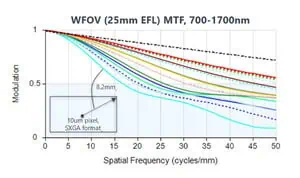
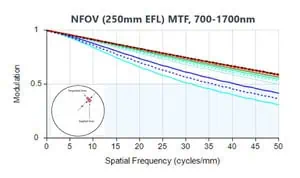
Performance Evaluation
Figures 1(a) and 1(b) depict the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) performance for wide-field (WFOV) and narrow-field (NFOV) zoom positions.
these graphs illustrate Sagittal (S) and Tangential (T) MTF components across spatial frequencies at various field positions for the SXGA 10 μm detector. The MTF remains high across the entire zoom range, particularly in narrow FOV (NFOV) positions, where fine detail is critical.
For the 5 μm sensor, the MTF, especially at narrow and medium FOV positions, approaches the diffraction limit, surpassing the performance of the 10 μm sensor.
This is attributed to the 5 μm sensor’s reduced maximum off-axis field (half that of the 10 μm) while doubling the cycle/mm from 50 to 100. Sagittal MTF remains close to the diffraction limit across the focal plane, although Tangential MTF is slightly lower, particularly in WFOV.
SupIR® (MWIR) 60-1200 mm f/4.0
The SupIR® MWIR lens excels in nighttime detection and provides robust performance in challenging environmental conditions, including smoke, haze, and high humidity.
With a detection range exceeding 28 km for vehicles, it is indeed well-suited for long-range surveillance and counter-unmanned aerial systems (C-UAS) applications.
This lens is compatible with 10 μm pixel, 1280×1024 SXGA format cooled MWIR cameras and maintains accurate line-of-sight and focus throughout the zoom range.
Key Advantages
- Compatible with 10 μm SXGA/HD detectors
- Continuous zoom with extended range
- Withstands severe shock and vibration
- Automatic focus compensation across temperature and zoom range
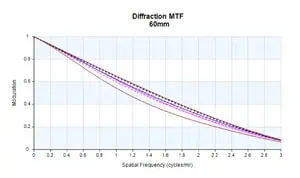
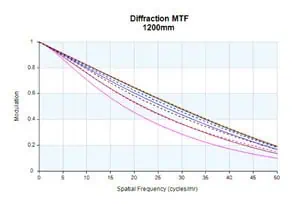
Performance Evaluation
As illustrated in Figure 2, MTF performance for this lens approaches the diffraction limit across the focal plane, particularly in WFOV. This high MTF level indicates sharp, high-resolution image quality throughout the zoom range.
SupIR (LWIR) 40-300 mm f/1.5
This LWIR lens utilizes thermal radiation emitted by objects,allowing detection without any external light source. It operates effectively in complete darkness and is less susceptible to glint in daylight.
Additionally, the LWIR lens performs well in adverse weather conditions. With a 7.5X zoom ratio, it offers a wide field of view, facilitating easy target acquisition and tracking.
The lens maintains sharp focus throughout its zoom range and provides a vehicle detection range exceeding 12.5 km.
It is indeed compatible with both 12 μm and 17 μm pixel pitch 1280×1024 SXGA format uncooled LWIR cameras, offering versatility for integration with various camera systems.
Key Advantages
- compatible with 12 μm pixel 1280×1024 SXGA uncooled LWIR cameras
- Passive athermalization for reliable performance across conditions
- Vehicle detection range exceeding 12.5 km
- High-durability, low-reflection hard-carbon AR coatings
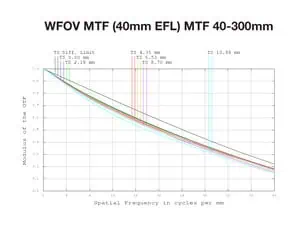
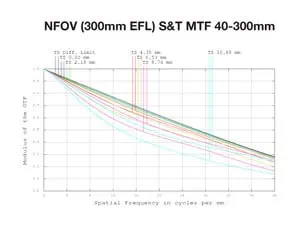
Performance Evaluation
Figure 3(a) displays MTF at WFOV (40mm) and Figure 3(b) at NFOV (300mm EFL).MTF performance remains high across the focal plane, particularly in WFOV, where off-axis MTF values are close to on-axis values, ensuring consistent image quality.
By integrating innovative optical designs, high-quality materials, and precise manufacturing, these lenses deliver extraordinary performance, durability, and adaptability for modern security and surveillance applications.
This extensive range of high-performance lenses meets the stringent demands of today’s operational environments, ensuring superior imaging across diverse and challenging conditions.




























